目录
Rigid-flex PCBs have gained prominence in various industries due to their unique combination of flexibility and durability. As a hybrid of flexible and rigid circuit boards, rigid-flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional PCB designs, making them a preferred choice in advanced electronics applications. This article will explore the benefits of rigid-flex PCBs, with an objective analysis of their performance, application areas, and potential drawbacks.
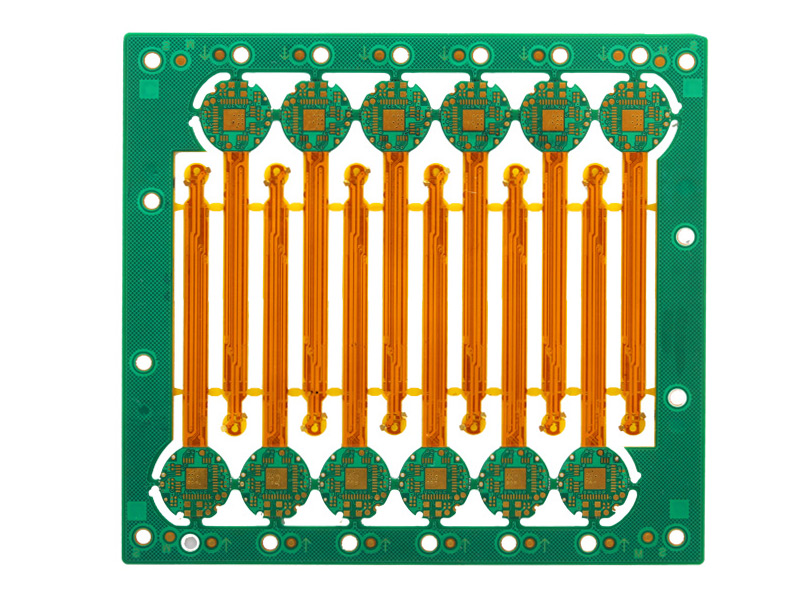
1. Space and Weight Efficiency
One of the most notable benefits of rigid-flex PCBs is their ability to save both space and weight. Traditional circuit boards often require connectors and cables to link various rigid boards together, which increases the weight and takes up significant space. In contrast, rigid-flex boards eliminate the need for these connectors and cables by incorporating flexible circuitry into a rigid board. This allows designers to create more compact and lightweight products.
For industries such as aerospace, military, and medical devices, where reducing the size and weight of electronics is critical, this feature of rigid-flex PCBs offers a significant advantage. Devices such as wearables, hearing aids, and implantable medical devices also benefit from this reduced bulk, making them more practical for everyday use.
2. Enhanced Durability
Another major advantage of rigid-flex PCBs is their increased durability. Traditional PCBs with connectors and cables are prone to failure from vibration, shock, and movement, as these components can loosen or break over time. Rigid-flex PCBs are more resistant to these mechanical stresses because they use fewer interconnects and have a solid structure combined with flexible areas that can withstand motion and bending.
This makes rigid-flex PCBs ideal for applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and defense, where products are frequently exposed to harsh environments. The reduced risk of mechanical failure also enhances the overall reliability and longevity of devices that incorporate rigid-flex designs.
3. Improved Signal Integrity
The elimination of connectors and cables in rigid-flex PCBs not only enhances durability but also improves signal integrity. In traditional PCB setups, signals must pass through multiple interconnects, which can introduce noise and increase the chances of signal degradation. Rigid-flex PCBs reduce the number of interconnects, allowing signals to travel more directly between components.
This reduction in signal interference and noise makes rigid-flex boards ideal for high-frequency applications or where signal integrity is crucial, such as in communication devices, aerospace systems, and sophisticated medical equipment.
4. Increased Design Flexibility
One of the key benefits of rigid-flex PCBs is their design flexibility. Engineers can incorporate both rigid and flexible layers into a single board, allowing for innovative designs that would not be possible with traditional PCBs. This flexibility enables the creation of complex, three-dimensional shapes, which can be folded, twisted, or bent to fit into unconventional spaces.
For consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables, this design freedom allows for sleeker and more ergonomic product designs. The ability to integrate multiple functionalities into a single rigid-flex board can also reduce the need for separate circuit boards, further streamlining product design and assembly.
5. Cost Efficiency in Complex Applications
Although rigid-flex PCBs are generally more expensive to produce than traditional PCBs, they can offer cost savings in the long run, particularly for complex, high-performance applications. The reduced need for connectors, cables, and solder joints can lower the overall material and assembly costs. Additionally, the increased reliability and durability of rigid-flex boards can reduce maintenance and repair costs over the product’s lifetime.
In industries where long-term performance and reliability are critical, such as aerospace and military applications, these potential cost savings make rigid-flex PCBs a practical investment despite their higher initial cost.
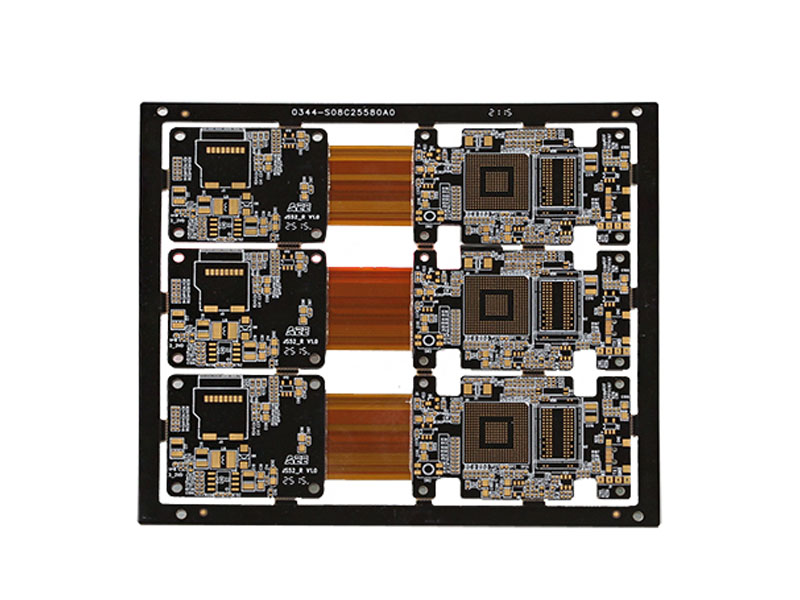
Conclusion
In summary, rigid-flex PCBs provide a versatile and efficient solution for modern electronics, especially in demanding applications. Their combination of space savings, durability, improved signal integrity, and design flexibility makes them a top choice for industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and consumer electronics. While their cost and complexity may be higher than traditional PCBs, the long-term benefits in terms of reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency make them an invaluable technology in cutting-edge product designs.
0









